Natural Gas Reserves in India
- Natural gas is a hydrocarbon gas mixture primarily composed of methane.
- It is a fossil fuel found in the same geological structure as petroleum.
- Sometimes natural gas forces oil to the surface, which is known as associated or wet gas.
- Gas found without oil is known as non-associated or dry gas.
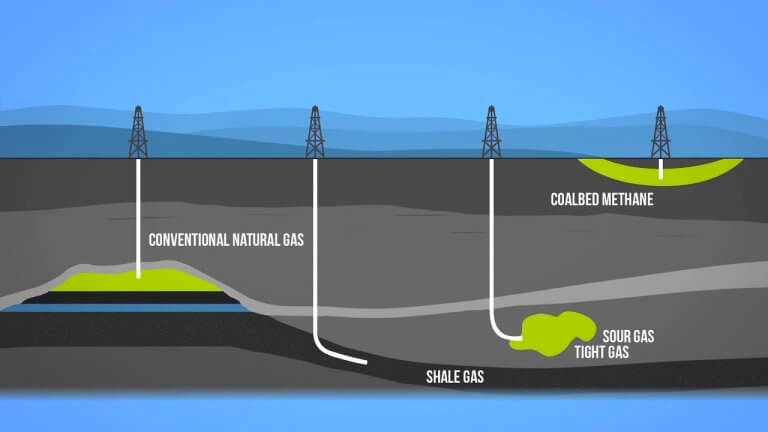
- Natural gas may contain hydrogen sulfide or other sulfur compounds, which is called sour gas.
- Coalbed methane is known as sweet gas due to its lack of hydrogen sulfide.
- Natural gas is typically bought and sold by calorific value, not volume, denoted as MMBTUs.
- Natural gas is odorless and colorless, but for safety reasons, mercaptan compounds are added for an odorization process.
- India’s commercial production of natural gas started much later (since 1961).
- The natural gas industry in India began in the 1960s with the discovery of gas fields in Assam and Gujarat.
- After the constitution of GAIL in 1984, there has been much emphasis on natural gas production.
Natural Gas Formation
- Natural gas is formed when layers of decomposing plant and animal matter are exposed to intense heat and pressure under the surface of the Earth over millions of years.
- The energy that the plants originally obtained from the sun is stored in the form of chemical bonds in the gas.
Uses of Natural Gas
- Industrial processes: Natural gas is used as a feedstock for chemical production and is also used in metal production, glass manufacturing, and other industrial processes.
- Refining: Natural gas is used as a fuel and a heat source in oil refineries.
- Fertilizers: Natural gas is a key input in the production of nitrogen fertilizers, such as ammonia and urea.
- Cooling: Natural gas is used as a refrigerant in liquefied natural gas (LNG) plants.
- Fuel for ships: Natural gas is used as a fuel for ships, either in compressed or liquefied form.
- Injection into pipelines: Natural gas is sometimes injected into pipelines to increase pressure and maintain flow.
- Backup power generation: natural gas-fired power plants are often used to provide backup power during periods of high demand or when renewable sources of energy are unavailable.
- Fuel for aircraft: Natural gas is being explored as a potential alternative fuel for aircraft, either in the form of LNG or as a component of synthetic jet fuel.
Importance of Natural Gas to India
- 40% of natural gas is consumed in fertilizer production
- 30% is used for power generation
- 10% is used for LPG
- Natural gas production has grown in all sectors since 1971
- Power stations using gas account for nearly 10% of India’s electricity
- Gas power stations in India are idle due to a lack of feedstock
- Existing plants are operating below capacity on expensive imported LNG
- India’s oil reserves are insufficient for growing energy needs
- Policy paralysis increases the gestation period of energy projects
- Diversification of energy sources is necessary to avoid external shocks
- Natural gas accounts for a quarter of global energy consumption
- In India, natural gas constitutes only 6% of the energy consumed
- The Indian government aims to increase the share of natural gas to 15% by 2030.
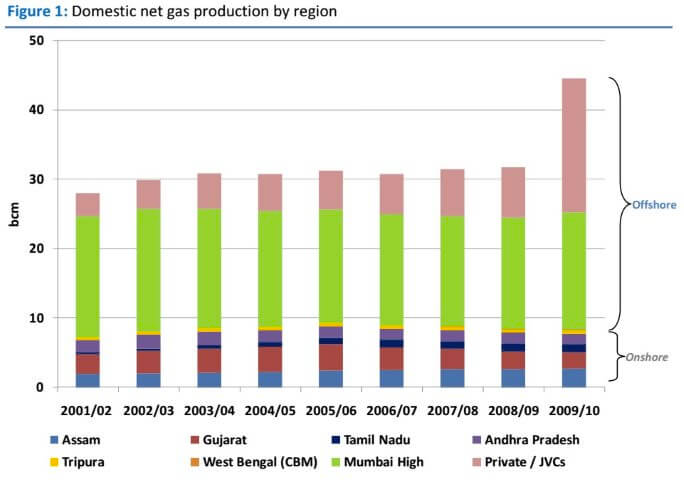
Distribution of Natural Gas in India
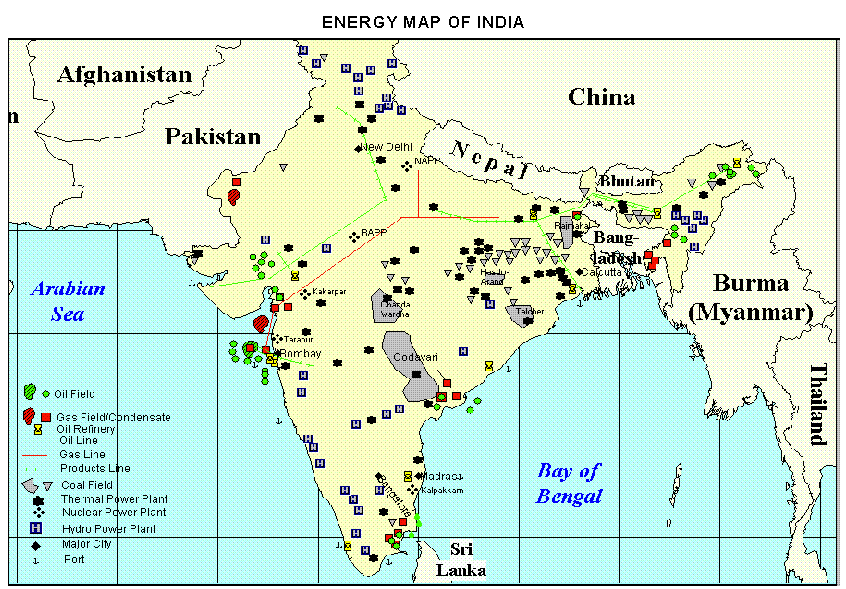
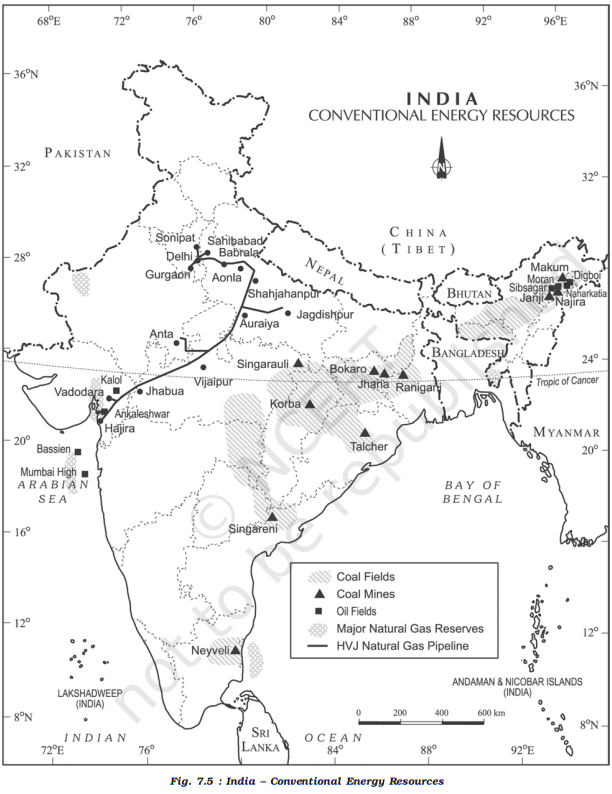
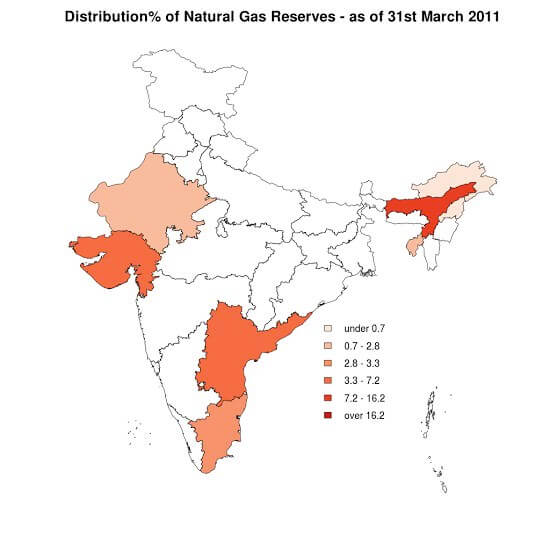
- Economically viable reserves of natural gas in India are located in Assam, Gujarat, Tripura, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The onshore reserves in Assam and Gujarat are estimated to be 541 BCM, with 190 BCM offshore in the Bay of Cambay and 190 BCM in Bombay High.
- A recent discovery in the Tripura Basin has reported a huge reserve of 400 BCM, with 72 BCM in the Rava structure.
- Remote sensing estimates suggest that the Andaman and Nicobar Islands have a reserve of around 1700 BCM, but its economic viability is yet to be established.
- These reserves have the potential to solve India’s energy needs for 100 years and could lead to an economic revolution in eastern India.
Natural gas and oil discoveries in India over the years:
- 1988-89: Oil strikes at Cauvery offshore and at Nanda in the Khambhat basin, and gas found in Tanot in the Jaiselmer basin in Rajasthan.
- 1988: Production from the South Bassein Gas Field started in September 1988.
- 1989-90: Oil/gas structures had been discovered in Adiyakkamanglam in Tamil Nadu, Andada in Gujarat, Khovaghat in Assam, Lingla in Andhra Pradesh, Mumbai Offshore, and Kachchh Offshore.
- 2002: Reliance Industries discovered the largest natural gas reserve in the world in the Krishna-Godavari offshore basin, estimated to be 14 trillion cubic feet.
- 2003: Gas and crude oil discovered in the Barmer district of Rajasthan.
- 2004: Reliance Industries discovered gas off the Orissa coast in the Bay of Bengal.
- 2005: Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) made a significant hydrocarbon find in the shallow waters of the Krishna Godavari basin, southwest of the Rava field discovered by ONGC in 1987.
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC)
- ONGC is a Maharatna Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) of the Government of India.
- It was established in 1995 and is under the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
- ONGC is the largest crude oil and natural gas company in India, contributing around 70% to Indian domestic production.
- It is the highest profit-making corporation in India, with a profit of USD 5 billion.
- ONGC is the largest Indian company in oil exploration.
- ONGC Videsh Ltd. (OVL) has a presence in 16 countries, especially in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, the CIS, and the Far East.
- OVL’s first overseas oil exploration project was the Rostam and Raksh oil fields in Iran.
- OVL’s first major oil find was the LanTay and LanDo oil fields in Vietnam.

0 Comments