- A sea is defined as a portion of the ocean that is partly surrounded by land.Seas have great geographical, political, and economical significance.
- In oceanography, a marginal sea is a sea partially enclosed by islands, archipelagos, or peninsulas.
Arabian Sea
- Located in the northern Indian Ocean, bordered by India, Oman, Pakistan, and Yemen.
- Important historical trade route connecting the Middle East, Africa, and South Asia.
- Influenced by monsoon winds, affecting marine life and navigation.
South China Sea
- One of the busiest maritime trade routes in the world, rich in natural resources.
- Contains numerous disputed islands and reefs among several countries.
- Supports diverse marine ecosystems including coral reefs and fisheries.
East China Sea
- Lies between China, Japan, and South Korea.
- Contains the Okinawa Trough, a deep oceanic trench.
- Subject to seasonal monsoons and typhoons.
Coral Sea
- Located off the northeast coast of Australia.
- Home to the Great Barrier Reef, the world’s largest coral reef system.
- Frequently affected by tropical cyclones.
Caribbean Sea
- Bordered by Central and South America and numerous island nations.
- Known for its clear blue waters and extensive coral reefs.
- Popular destination for tourism, shipping, and fishing.
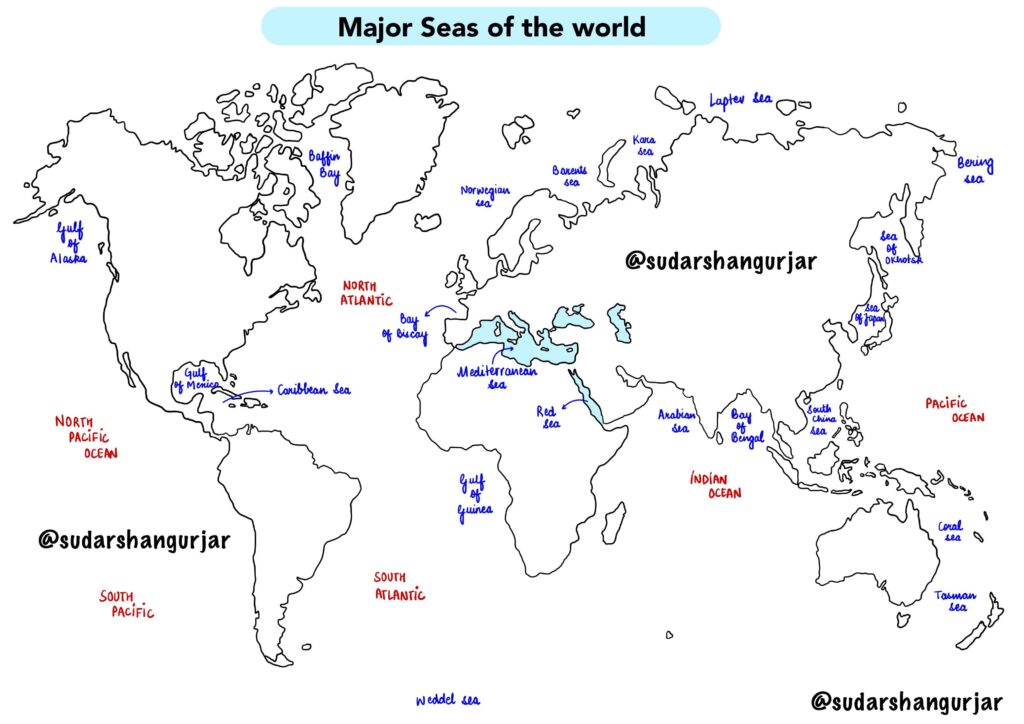
Mediterranean Sea
- Almost entirely enclosed by Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Historically significant as a cradle of ancient civilizations and trade.
- Characterized by warm, salty waters and diverse marine life.
Ionian Sea
- Positioned between southern Italy, Sicily, and western Greece.
- Known for deep waters and numerous islands.
- Popular for tourism and maritime activities.
Bay of Bengal
- Northeast part of the Indian Ocean, bordered by India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and others.
- Prone to cyclones and heavy monsoon rains.
- Receives freshwater inflow from major rivers like the Ganges and Brahmaputra.
Bering Sea
- Located between Alaska and Russia.
- Rich in marine biodiversity and commercial fisheries.
- Contains the Bering Strait, a key passage between the Arctic and Pacific Oceans.
Sea of Okhotsk
- Situated off the eastern coast of Russia.
- Experiences sea ice cover in winter.
- Important fishing grounds and habitat for marine mammals.
Gulf of Mexico
- Surrounded by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba.
- Major oil and gas production region.
- Frequently impacted by hurricanes.
Tasman Sea
- Lies between Australia and New Zealand.
- Known for rough seas and strong winds.
- Important for shipping and marine biodiversity.
Hudson Bay
- Large inland sea in northeastern Canada.
- Shallow and ice-covered for much of the year.
- Habitat for polar bears and migratory birds.
Sea of Japan
- Bordered by Japan, Russia, and Korea.
- Rich fishing grounds and important shipping route.
- Subject to territorial disputes between bordering nations.
Sea of Azov
- Connected to the Black Sea via the Kerch Strait.
- Shallowest sea in the world.
- Important for fisheries and regional transportation.
Caspian Sea
- Largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth.
- Borders five countries including Russia, Iran, and Kazakhstan.
- Rich in oil and natural gas reserves.
Adriatic Sea
- Lies between Italy and the Balkan Peninsula.
- Known for its clear waters and numerous islands.
- Popular tourist destination with historic coastal cities.
Baltic Sea
- Enclosed by Scandinavia, Finland, and the Baltic states.
- Brackish water due to limited connection with the Atlantic Ocean.
- Sensitive to pollution and eutrophication.
Red Sea
- Between northeast Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
- One of the warmest and saltiest seas.
- Famous for its extensive coral reefs.
Yellow Sea
- Located between China and the Korean Peninsula.
- Shallow with high sediment deposits from major rivers.
- Important for fishing and shipping.
Dead Sea
- Landlocked salt lake between Jordan and Israel.
- One of the saltiest bodies of water on Earth.
- Lowest point on Earth’s surface, famous for therapeutic mud.
Black Sea
- Surrounded by Eastern Europe and Western Asia.
- Contains a large anoxic (oxygen-free) layer below the surface.
- Important for regional trade and fisheries.
Tyrrhenian Sea
- Part of the Mediterranean, west of Italy.
- Deep basin with volcanic activity nearby.
- Popular for tourism and sailing.
Ligurian Sea
- Located between northwestern Italy and the island of Corsica.
- Known for deep waters and rich marine biodiversity.
- Includes the famous Cinque Terre coastline.
Balearic Sea
- Western Mediterranean, near the Balearic Islands of Spain.
- Popular for tourism and recreational boating.
- Part of a biologically diverse marine region.
Alboran Sea
- Westernmost part of the Mediterranean, between Spain and Morocco.
- Acts as a transition zone between the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea.
- Influenced by complex water currents.
Sargasso Sea
- Located in the North Atlantic Ocean, defined by surrounding currents.
- Unique for its floating mats of Sargassum seaweed.
- Important spawning ground for eels and other marine species.
Aegean Sea
- Between Greece and Turkey.
- Contains thousands of islands and islets.
- Historically significant as the cradle of ancient Greek civilization.
Philippine Sea
- Largest sea in the world by area, located east of the Philippines and Taiwan.
- Bordered by the Philippines, Taiwan, Japan, and the Marianas; contains the Mariana Trench, the world’s deepest oceanic trench.
- Known for frequent typhoons and rich marine biodiversity, including coral reefs and tuna fisherie
North Sea
- Bordered by the UK, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France.
- Major center for offshore oil and natural gas extraction.
- Important for fishing, shipping, and wind energy development.
Norwegian Sea
- Lies between Norway, Iceland, and the Svalbard archipelago.
- Influenced by the warm North Atlantic Current, keeping it mostly ice-free year-round.
- Rich in marine life, including whales, cod, and herring.
Barents Sea
- Located north of Norway and Russia, part of the Arctic Ocean.
- Ice-covered in winter but increasingly navigable due to climate change.
- Noted for rich fisheries and significant oil and gas reserves.
Gulf of Aden
- Connects the Red Sea to the Arabian Sea, bordered by Yemen and Somalia.
- Vital shipping route as part of the Suez Canal pathway.
- Known for piracy issues in the early 21st century.
Persian Gulf
- Located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.
- Contains some of the world’s largest oil reserves and export terminals.
- Warm, shallow waters with high salinity and unique marine life.
Gulf of Thailand
- Bordered by Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam.
- Shallow, warm waters support extensive fishing and tourism industries.
- Prone to seasonal monsoon rains and occasional tropical storms.
Andaman Sea
- Lies between the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the coast of Myanmar and Thailand.
- Known for its clear waters, coral reefs, and popular tourist destinations like Phuket.
- Important for regional shipping and fishing.
Bismarck Sea
- Located north of Papua New Guinea in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
- Named after German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck.
- Rich in tuna fisheries and subject to volcanic and seismic activity.
Solomon Sea
- Situated between Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.
- Known for World War II naval battles and significant marine biodiversity.
- Deep waters with active tectonic zones and frequent earthquakes.
Beaufort Sea
- Part of the Arctic Ocean, north of Alaska and Canada.
- Covered by sea ice for most of the year, but increasingly open during summer.
- Contains significant oil and gas potential and is a habitat for polar bears and whales.
Laptev Sea
- Located in the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia, Russia.
- Known for its extreme cold and large seasonal ice cover.
- Important source of freshwater to the Arctic due to river inflows.
Chukchi Sea
- Lies between Alaska and Russia, north of the Bering Strait.
- Seasonal sea ice cover, with increasing interest in shipping and resource extraction.
- Important for indigenous communities and Arctic wildlife.
White Sea
- An inlet of the Barents Sea, located in northwest Russia.
- Freezes over in winter; important for Russian shipping and fishing.
- Major port: Arkhangelsk.

0 Comments