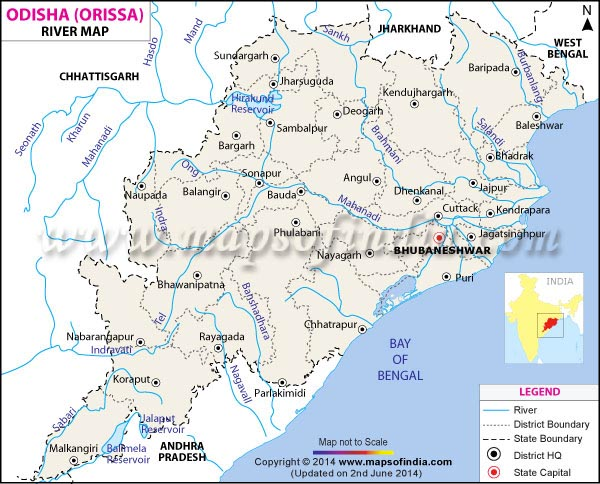
Mahanadi River – The Mahanadi River system is the third largest of peninsular India and the largest river of Odisha state. The word Mahanadi is a compound of the two Sanskrit words maha, which means means ”great” and nadi, which means ”river.”
Mahanadi River system
- Mahanadi River Basin Area and Coverage – The Mahanadi basin spans across Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh, covering an area of 1.4 lakh sq. km.
- Mahanadi Basin Boundaries – It is bounded by the Central India hills on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and east, and by the Maikala range on the west.
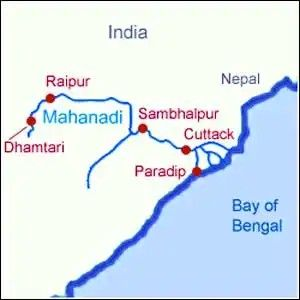
- Mahanadi originates from – The Mahanadi river flows for a total of 560 miles (900 km) and has its source in Raipur District of Chhattisgarh.
- Mahanadi River Rank – It is the second-largest river in terms of water potential and flood-producing capacity after the Godavari.
- Mahanadi River Streams – Small streams between the Mahanadi and the Rushikulya that drain directly into the Chilka Lake also form part of the basin.
- Mahanadi Basin Land Use – Over 54% of the basin is covered with agricultural land.
- Silt in Mahanadi River – The Mahanadi river is one of the most active silt-depositing streams in the Indian subcontinent.
- Mahanadi Flows in Which District of Odisha – At Sambalpur in Odisha, the Hirakud Dam has been constructed on the river, forming a man-made lake that is 35 miles (55 km) long.
- Mahanadi River Route – The river enters the Odisha plains near Cuttack and empties into the Bay of Bengal at False Point via several channels.
- Puri, located at one of the river’s mouths, is a famous pilgrimage site.

Tributaries of Mahanadi River
- Its upper course lies in the saucer-shaped basin called the ‘Chhattisgarh Plain’.
- This basin is surrounded by hills on the north, west, and south as a result of which a large number of tributaries join the main river from these sides.
- Left bank tributaries: The Seonath, the Hasdeo, the Mand, and the Ib.
- Right bank tributaries: The Ong, the Tel, and the Jonk.
SEONATH:
- Originates from Panabaras Hill (625 m)
- Flows towards the north-east
- Feeds the inhabitants and industries of Durg District
- Total length is 345km
HASDEO:
- River originates from Chhattisgarh
- Total length is 333km and the drainage area is 9856sqkm
- Flows towards the south of Chhattisgarh, through Bilaspur and Korba Districts
- Along the river lie rocks and hilly areas, thin forest areas
MAND:
- Left-bank tributary of Mahanadi
- Joins Mahanadi in Chandrapur before the river reaches Hirakud dam
- Total length is 241sqkm
- Drains an area in the range of 5200sqkm
- Mand River dam has been constructed in the Raigarh district of Chhattisgarh
IB:
- Left-bank tributary of Mahanadi River
- Originates in hills in Raigarh district of Chhattisgarh
- River runs for a distance of about 252km and drains an area of 12,447sqkm
- Ib river valley is famous for its rich coal belt
ONG:
- Right-bank tributary of the Mahanadi river
- Flows across Orissa and joins Mahanadi at Sambalpur 11km up-stream of Sonepur where Tel merges
- Drains an area of about 5128sqkm
TEL:
- Originates in the Nabarangpur district
- Flows through the Kalahandi, Balangir, and Sonpur districts of Orissa
- Second-largest river of Orissa
Kathajodi River:
- An arm of the Mahanadi River in Odisha
- Branches off at Naraj and immediately bifurcated
- Southern branch is known as Kuakhai, flows into the Puri district
- Mouth is closed by a bar, little water flows except at flood times
- Bifurcated again at Cuttack into Sidhua (right branch) and Khatajodi (left branch)
- Cuttack City is situated between Mahanadi and Kathajodi
- Other distributaries of Mahanadi include Paika, Birupa, Chitroptala river, Genguti, and Lun
Sukapaika River:
- One of several distributaries of Mahanadi river in Odisha
- Branches away from Mahanadi at Ayatpur village in Cuttack district
- Flows for about 40 kilometers (km) before rejoining Mahanadi at Tarapur in the same district
- Drains a large landmass comprising over 425 villages
- Covers three blocks: Cuttack Sadar, Raghunathpur, and Nichintakoili of Cuttack
- Important system of Mahanadi to control floodwater and maintain flow in the river as well as the Bay of Bengal
- River is undergoing sudden barrenness
Chitroptala River:
- River in Odisha, India
- Distributary of the Mahanadi, situated in both Kendrapara and Cuttack districts.
.
Important cities
Projects on Mahanadi River:
- Mahanadi main canal and Tandula reservoir were completed during the pre-plan period.
- During the plan period, the Hirakud dam, Mahanadi Delta Project, the Hasdeo Bango, and the Mahanadi Reservoir Project were completed.
- Hirakud Dam aims at controlling floods in the Mahanadi basin, providing water for irrigation and municipal water supply.
Industry in Mahanadi River Basin:
- Raipur, Durg, and Cuttack are important urban centers in the basin.
- The Mahanadi basin has a favorable industrial climate due to its rich mineral resources adequate power resources
- Important industries are the iron and steel plant at Bhilai, aluminum factories at Hirakud and Korba, a paper mill near Cuttack, and a cement factory at Sundargarh.
- Other industries are sugar and textile mills.
- Mining of coal, iron, and manganese are other industrial activities.
Floods in Mahanadi River Basin:
- The basin is subject to severe flooding occasionally in the delta area due to the inadequate carrying capacity of the channels.
- Hirakud Dam provides some amount of flood relief by storing part of the floodwater, but a lasting solution needs to be developed.

0 Comments