- Biomass is organic material from plants and animals.
- Biomass energy is produced by living or once-living organisms.
- Biomass is used for cooking and heating in developing countries.
- Biomass fuels are used to avoid carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel use.
- Plants produce biomass through photosynthesis, which contains stored chemical energy from the sun.
- Biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to renewable fuels.
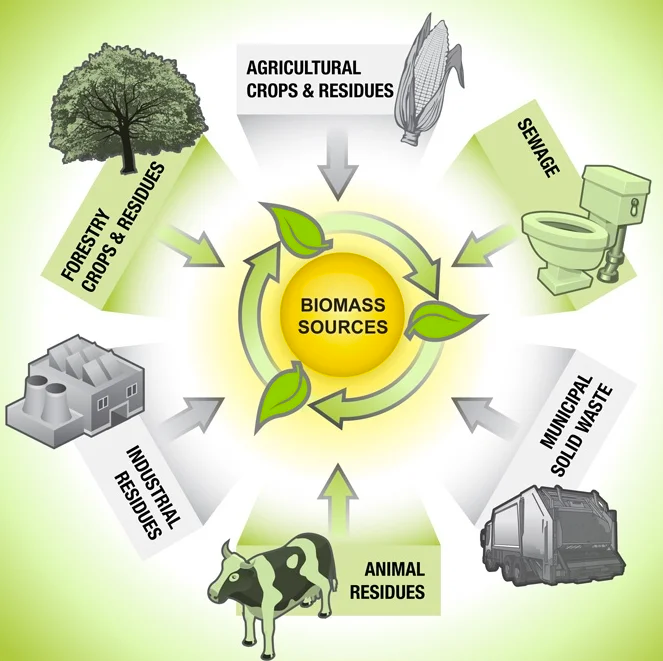
- Biomass sources include wood, wood processing wastes, agricultural crops and waste materials, biogenic materials in municipal solid waste, animal manure, and human sewage.
Converting biomass to energy
- Biomass can be converted to energy through different processes.
- Direct combustion is the most common method, burning biomass to produce heat for buildings, water, and electricity.
- Thermochemical conversion uses pyrolysis and gasification to produce solid, gaseous, and liquid fuels.
- Chemical conversion uses transesterification to produce biodiesel from vegetable oils, animal fats, and greases.
- Biological conversion uses fermentation to produce ethanol and anaerobic digestion to produce renewable natural gas.
- Renewable natural gas is produced in anaerobic digesters at sewage treatment plants and dairy/livestock operations.
- Biomethanation decomposes biodegradable matter, producing methane-rich biogas.
- Cogeneration produces two forms of energy from one fuel, generating heat and electricity or mechanical energy.
- Conventional power plants have an efficiency of around 35%, while cogeneration plants can reach 75%-90% efficiency.
- Cogeneration can meet power and heat needs, resulting in significant cost savings and reduced emissions of pollutants.
Advantages of Biomass Energy:
- Versatile
- Renewable
- No net CO2 emissions (ideally)
- Emits less SO2 and NOx than fossil fuels
Disadvantages of Biomass Energy:
- Low energy density/yield:
- Some biofuels, like Ethanol, is relatively inefficient as compared to gasoline. In fact, it has to be fortified with fossil fuels to increase its efficiency. In some cases (e.g. corn-derive bioethanol) may yield no net energy.
- Land conversion:
- Land needed to produce biomass may be in demand for other purposes such as conservation or housing or agriculture use which may lead to a possible decrease in agricultural food production. It may also lead to biodiversity loss.
- Apart from the above there are usually problems associated with intensive agriculture like:
- Nutrient pollution
- Soil depletion
- Soil erosion
- Other water pollution problems
- Possible decrease in agricultural food production
- Biodiversity loss
Bio-energy role meeting India’s energy demands:
- Meets growing demand for energy, especially in rural areas
- Mitigates climate change by reducing GHG emissions
- Market for renewable energy systems is set to grow exponentially
- Waste-to-energy potential can help achieve renewable energy goals
- Generates income and employment opportunities for farmers
- Reduces imports and improves energy security and self-reliance
Various Government efforts in reaping Bioenergy:
- 10 GW national target:
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has set a national target to achieve 10 GW of installed biomass power by 2022.
- National Policy on Biofuels:
- The policy is aimed at achieving 20% blending of biofuels with fossil-based fuels by 2025.
- Policy for biomass and bagasse cogeneration:
- MNRE has developed a policy for biomass and bagasse cogeneration that includes financial incentives and subsidies for biomass projects and sugar mills that use this technology.
- Fiscal incentives:
- The government provides various fiscal incentives such as 10 years income tax holidays, concessional customs and excise duty exemption for machinery and components for initial setting up of biomass power projects, and general sales tax exemption in certain states.
- Waste to energy projects:
- Waste to energy projects are being set up for generation of energy from urban, industrial and agricultural waste such as vegetable and other market wastes, slaughterhouse waste, agricultural residues and industrial wastes & effluents.
- National Biomass Repository:
- MNRE plans to create a ‘National Biomass Repository’ through a nation-wide appraisal program to ensure availability of biofuels produced from domestic feedstock
National Mission on use of Biomass in coal-based thermal power plants
- Ministry of Power has set up a National Mission on Biomass in coal-based thermal power plants.
- Aim is to address air pollution due to farm stubble-burning and reduce carbon footprints of thermal power generation.
- It will contribute to the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
- The objective is to increase co-firing from the present 5% to higher levels for carbon-neutral power generation.
- Co-firing involves adding biomass as a partial substitute fuel in high-efficiency coal boilers.
- R&D will be taken up for boiler design to handle higher amounts of silica and alkalis in biomass pellets.
- Mission will facilitate overcoming constraints in the supply chain of biomass pellets and agro-residue and their transport to power plants.
- Regulatory issues in biomass co-firing will also be considered.

0 Comments