- The Brahmaputra means “son of Brahma.”
- Source of Brahmaputra River – Its source is the Chemayungdung glacier in southwestern Tibet, close to the sources of Indus and Satluj.
- Mariam La separates its source from the Manasarovar Lake.
- Brahmaputra River System – It passes through the depression formed by the Indus-Tsangpo Structure Zone in Tibet.
- Despite its high altitude, the Tsangpo has a gentle slope and a wide navigable channel for about 640 km.
- Brahmaputra River Length – receives many tributaries in Tibet, the first major one being the Raga Tsangpo.
- It flows across southern Tibet as the Yarlung Tsangpo River, breaks through the Himalayas in great gorges, and enters Arunachal Pradesh where it’s known as Dihang.
- Just west of the town of Sadiya, it is joined by two mountain streams, the Lohit and the Dibang, and is then known as the Brahmaputra.
- Brahmaputra River Flows Through Which States – It flows through Bangladesh as the Jamuna and merges with the Ganga to form the Sunderbans delta.
- Brahmaputra River Tributaries – The biggest and smallest river islands in the world, Majuli and Umananda respectively, are in the river in the state of Assam.
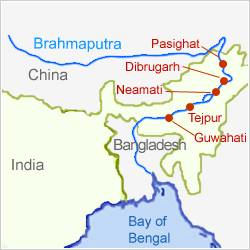
- Important Urban Centers Along the Brahmaputra River- Dibrugarh, Pasighat, Neamati, Tezpur, and Guwahati are important urban centers along the river.

| Region | Name |
| Tibet | Tsangpo (meaning ‘The Purifier’) |
| China | Yarlung Zangbo Jiangin |
| Assam Valley | Dihang or Siong, South of Sadiya: Brahmaputra |
| Bangladesh | Jamuna River |
| Bangladesh | Padma River: Combined Waters of Ganga and Brahmaputra |
| Bangladesh | Meghana: From the confluence of Padma and Meghna |
Major Tributaries of the Brahmaputra River

Left Bank Tributaries of Brahmaputra River
Some of the main rivers joining the Brahmaputra from the left are
- Lhasa River
- Nyang River
- Parlung Zangbo River
- Lohit River
- Dhanashri River
- Kolong River
Lohit River
- Originates in eastern Tibet.
- Flows through the Mishmi hills to meet the Siang at the head of Brahmaputra valley.
- The valley of Lohit is thickly forested, covered with alpine and sub-tropical vegetation.
- A large variety of medicinal plants are also found here.
Dhansiri River
- Main river of Golaghat District of Assam and Dimapur District of Nagaland.
- Originates from Nagaland.
- Numerous perennially waterlogged swampy regions associated with this river.
Right Bank Tributaries of Brahmaputra River
Some of the main rivers joining the Brahmaputra from the right are:
- Subansiri River
- Kameng River
- Manas River
- Beki River
- Raidak River
- Jaldhaka River
- Teesta River
Subansiri River
- Subansiri River is also called as Gold River as it is famous for its gold dust.
- It flows through the Lower Subansiri District in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Subansari, a swift river offers excellent kayaking opportunities.
Kameng River
- Kameng River originates in Tawang district in the eastern Himalayan mountains.
- It flows through West Kameng District in Arunachal Pradesh and Sonitpur District in Assam.
- The river forms the boundary between East Kameng District and West Kameng Districts.
- Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary and Kaziranga National Park are located near the Kameng River.

Manas River
- The Manas River flows through southern Bhutan and India.
- It is 376 km long, with 272 km in Bhutan and 104 km in Assam.
- The river meets the Brahmaputra River at Jogighopa.
- The area around the river has two major forest reserves: Royal Manas National Park in Bhutan and Manas Wildlife Sanctuary in India.
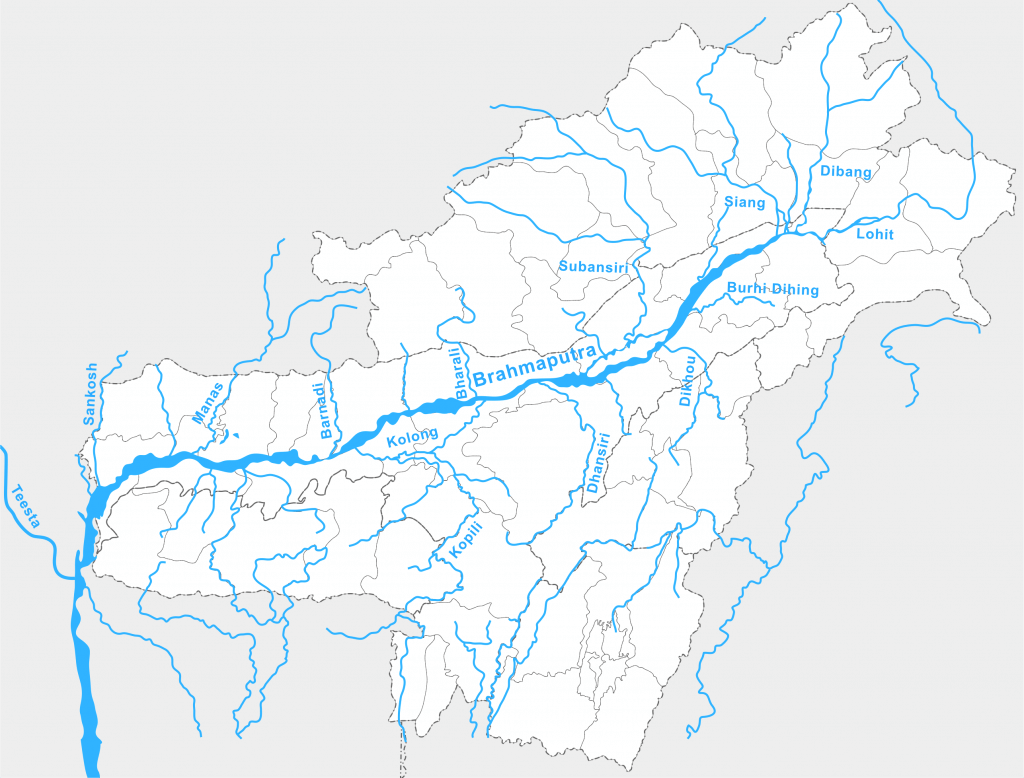
Sankosh River
- It rises in northern Bhutan and empties into the Brahmaputra in the state of Assam
- The upper catchment of the river is glaciated. The middle and the lower courses flow along V-shaped valleys that have been carved by running water
- The entire catchment of the river is covered with forests.
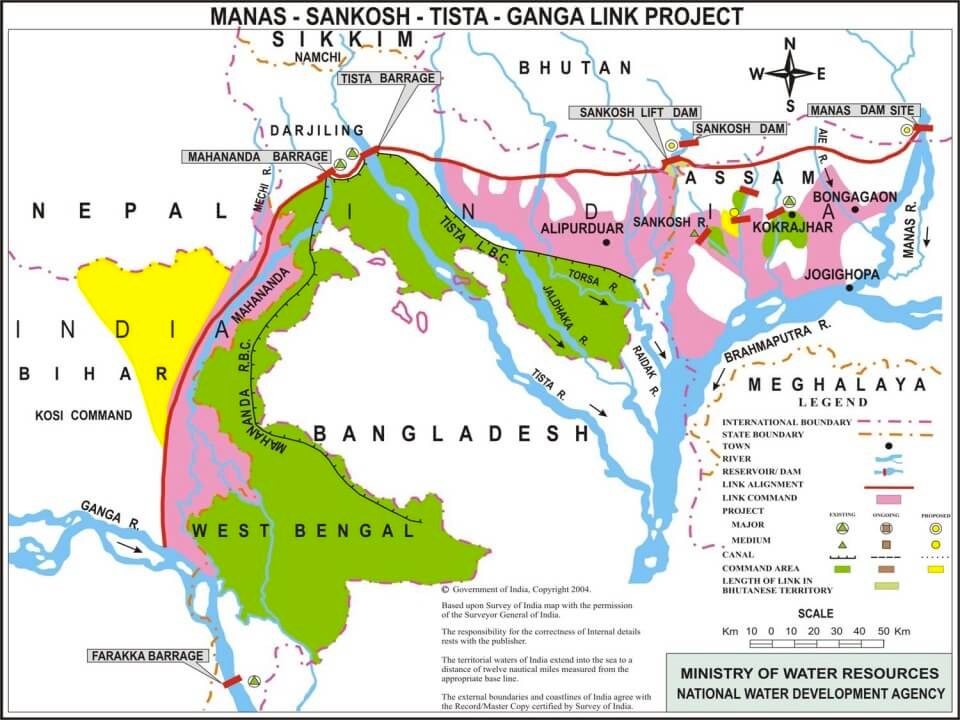
Teesta River
- Originates from Tso Lhamo lake in North Sikkim, Himalayas
- Rangeet River is its major tributary and largest river in Sikkim
- Rangeet river joins Teesta river at Tribeni
- Flows past Rangpo forming border between Sikkim and West Bengal up to Teesta Bazaar
- Flows through Jalpaiguri before reaching Rangpur District, Bangladesh
- Merges with the Brahmaputra river
Dibang River
- The Dibang River is a major tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- It originates from the southern slope of the Himalayas near the Tibet border at an altitude of over 5000m.
- The river enters the plains near Nizamghat in the Lower Dibang Valley district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The upper course of the Dibang River is located in the Mishmi hills.
Kopili River:
- Interstate river in Northeast India that flows through the states of Meghalaya and Assam.
- Largest south bank tributary of the Brahmaputra in Assam.
- Carissa Kopilii (Plant Species) is distributed sparsely along the Kopili riverbed.
- The plant is threatened by a hydroelectric project on the river and water turned acidic because of coal mining in Meghalaya upstream.
Siyom River
- Right tributary of the Brahmaputra.
- Rises on the south of the main ridge of the Assam Himalaya near the Tibet border.
- Mouling National Park is located on the east bank of the river.
- Flows initially in a southerly direction, later in an easterly and southerly direction through the West Siang District.
- Saje River is the most prominent among its several tributaries.
- Siyom Bridge:
- State-of-the-art 100-meter long, Class 70 Steel Arch Superstructure over Siyom River in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Holds great strategic significance in tackling China as it serves as a gateway to sensitive areas of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in Arunachal Pradesh.
Important cities on Brahmaputra
Major River Valley Projects/Dams/Barrages associated with the Brahmaputra river system-
- In the state of Arunachal Pradesh-
- Tawang Hydel Power Project
- Subansiri Lower Hydel Power Project
- Ranganadi Hydel Power Project
- Paki Hydel Power Project
- Papumpap Hydel Power Project
- Dhinkrong Hydel Power Project
- Upper Lohit Hydel Power Project
- Damway Hydel Power Project
- Kameng Hydel Power Project
- In the state of Sikkim-
- Rangit Hydel Power Project
- Teesta Hydel Power Project
- In the state of Assam-
- Kopli Hydel Power Project
- In the state of Meghalaya-
- New Umtru Hydel Power Project
- In the state of Nagaland-
- Doyang Hydel Power Project
- In the state of Manipur-
- Loktak Hydel Power Project
- Tipaimukh Hydel Power Project
- In the state of Mizoram-
- Tuibai Hydel Power Project
- Tuirial Hydel Power Project
- Dhaleshwari Hydel Power Project

0 Comments