- Rivers have been important throughout human history.
- Water from rivers is essential for various human activities.
- Riverbanks have attracted settlers from ancient times.
- Rivers are used for irrigation, navigation, and hydropower generation.
- India relies on rivers for agriculture, which is the major source of livelihood for the majority of its population.
- Major east-flowing rivers in India include Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery, Mahanadi, Pennar, Subarnarekha, Brahamani, Ponnaiyar, and Vaigai River.
- East flowing rivers in India flow into the Bay of Bengal.
- East flowing rivers in India have many tributaries and form deltas.
- East flowing rivers in India carry larger sediments than West flowing rivers.
Pennar River
- The Pennar river is also known as Uttara Pinakini and is one of the major rivers of the Indian peninsula.
- pennar river originates from – It originates in the Chennakasava hill of the Nandidurg range in Chikkaballapura district of Karnataka.
- The river flows towards the east and eventually drains into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Pennar river has a total length of 597 km.
- The Pennar basin extends over the states of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka and covers an area of approximately 55 thousand sq.km.
- The basin is fan-shaped and is bounded by the Erramala range on the north, the Nallamala and Velikonda ranges of the Eastern Ghats on the east, the Nandidurg hills on the south, and a narrow ridge on the west.
- The Seshachalam and Paliconda ranges are other hill ranges in the basin to the south of the river.
- The major part of the basin is covered with agriculture, accounting for 58.64% of the total area.
- Tributaries of Pennar River:
- Left Bank: the Jayamangali, the Kunderu and the
- Right bank: the Chiravati, the Papagni, etc.
- Projects on Pennar River:
- Tungabhadra high-level canal in Krishna basin irrigated areas in Pennar basin also. The major project in the basin is the Somasila project, Mylavaram Dam, Penna Ahobilam Balancing Reservoir (PABR Dam).
Palar River
- Palar is a river in southern India.
- It originates from the Nandi Hills in Chikkaballapura district of Karnataka state and flows through Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- The river eventually reaches the Bay of Bengal at Vayalur.
- The Cheyyar and Ponnai rivers are the major tributaries of the Palar river in Tamil Nadu.
- Water from the Palar anicut is diverted to the Poondi reservoir located in the Kosasthalaiyar River basin and to Chembarambakkam Lake located in the Adayar River basin.
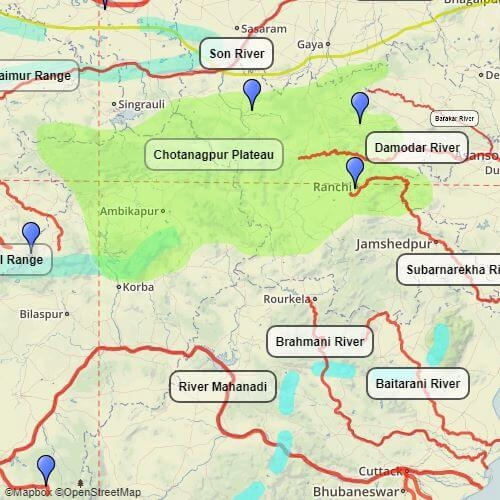
Subarnarekha River
- The Subarnarekha River originates from the Ranchi Plateau in Jharkhand and forms the boundary between West Bengal and Odisha in its lower course.
- It eventually joins the Bay of Bengal, forming an estuary between the Ganga and Mahanadi deltas.
- The total length of the Subarnarekha River is 395 km.
- The Dulang River is a tributary of the Subarnarekha River on the left bank.
- The Kanchi River, Kharkai, Karkari River, Raru River, and Garru River are tributaries of the Subarnarekha River on the right bank.
- Hundru Falls is created on the course of the Subarnarekha, where it falls from a height of 98 metres (322 ft).
Brahmani River
- The Brahmani River originates from the confluence of the Koel and the Sankh rivers near Rourkela.
- The river has a total length of 800 km.
- The Brahmani River basin is bounded by the Chhotanagpur plateau in the north, the Mahanadi basin in the west and south, and the Bay of Bengal in the east.
- The basin flows through the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha before draining into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Brahmani River, along with the Baitarani River, forms a large delta before emptying into the Bay of Bengal at Dhamra.
- Rengali dam is a dam located in Odisha, India. It is constructed across the Brahmani River in Rengali village, located 70 km from Angul in Angul district.
Baitarni River
- The Baitarani River is a major river in the state of Odisha.
- The river basin lies mostly in Odisha, except for a small portion in the Singhbhum District of Jharkhand.
- The Baitarani River originates from the Guptaganga hills in Keonjhar District of Odisha.
- Initially, the river flows in a northern direction for about 80 km before taking a sudden right turn.
- In this reach, the river serves as a boundary between the states of Jharkhand and Odisha up to the confluence of Kangira River.
Damodar
- The Damodar River rises in the Palamau hills of Chota Nagpur at an elevation of about 609.75 m
- It flows through a rift valley in a south-easterly direction
- It enters the deltaic plains below Raniganj
- Near Burdwan, the river abruptly changes its course to a southerly direction
- The Damodar River joins Hooghly about 48.27 km below Calcutta
- It has several tributaries and subtributaries, including Barakar, Konar, Bokaro, Haharo, Jamunia, Ghari, Guaia, Khadia, and Bhera
- The biggest tributary of the Damodar River is the Barakar, which originates in the Hazaribagh district
- Earlier known as the Sorrow of Bengal because of its ravaging floods in the plains of West Bengal
- The Damodar River is now the most contaminated river in India due to various industries on its riverbanks
- The industries on its riverbanks are good resources of minerals, including coal-oriented industries
- Several coal-oriented industries are scattered over the Damodar basin
Ponnaiyar River
- The South Pennar River is known as Dakshina Pinakini in Kannada and Thenpennai in Tamil, and also referred to as Ponnaiyar.
- It originates in the Nandi Hills in the Chikkaballapura district of Karnataka and flows through Tamil Nadu before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.
- The river basin covers a small area in the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- The basin is bounded on the North-West and South by various ranges of the Eastern Ghats, and in the East by the Bay of Bengal.
- The Krishnagiri dam and Sathanur Dam are built across this river, and the Moongilthuraipattu Sugar Factory is situated on the bank of the river.
Vaigai River
- The Vaigai is a river in Tamil Nadu, India.
- It originates in Varusanadu Hills, the Periyar Plateau of the Western Ghats range and flows northeast through the Kambam Valley.
- Vattaparai Falls are located on this river.
- The river empties into the Palk Strait near Uchipuli, close to the Pamban bridge in Ramanathapuram District.
- Its main tributaries are Suruliyaru, Mullaiyaru, Varahanadhi, Manjalaru, Kottagudi, Kridhumaal, and Upparu.
- The Suruliyar and Manjalar are important left-bank tributaries.
- The Vaigai also receives a minor tributary, the Varahanadhi, on its left bank below the Vaigai dam.
- The Vaigai flowed through the ancient city of Madurai, the capital of the Pandya kingdom.
- It finds a mention in Sangam literature dated to 300 BCE.

0 Comments