Petroleum
- Crude petroleum is a mixture of hydrocarbons, including solids, liquids, and gases
- Compounds in petroleum include paraffin and unsaturated hydrocarbons, as well as a small proportion of benzene group compounds
- Petroleum and petroleum products are mainly used as motive power for transportation on land, in the air, and on water
- Petroleum is a convenient and compact liquid fuel that can be easily transported by tankers or pipelines
- Petroleum emits little smoke and leaves no ash, making it a cleaner fuel than coal
- It can be used up to the last drop and is an important source of lubricating agents
- Petroleum is also used as a raw material for various petrochemical products.
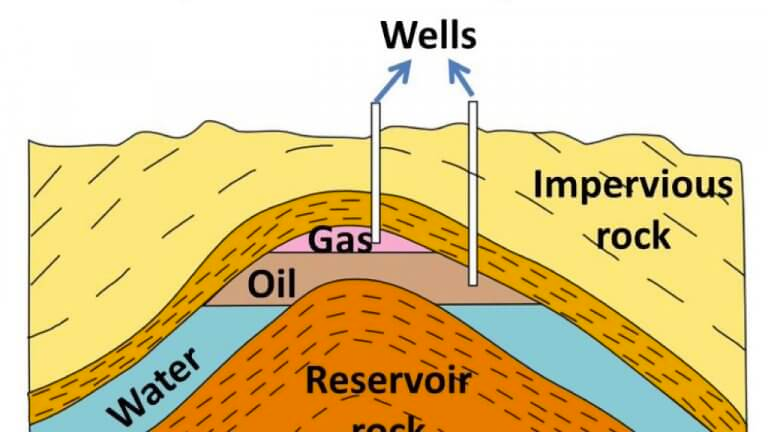
Origin and Occurrence
- Petroleum has an organic origin and is found in sedimentary basins and shallow depressions
- Oil reserves in India are associated with anticlines and fault traps in sedimentary rock formations of tertiary times
- Recent sediment also shows evidence of incipient oil
- An oil reservoir must have porosity, permeability, and be capped by impervious beds
- Porous sandstone, conglomerates, and fissured limestone containing oil should be capped by impervious beds
- Petroleum is mainly found in Miocene rocks (e.g. Mumbai High) and mid-folding rocks
- Petroleum and its products are used as a compact and convenient liquid fuel for transportation on land, air, and water
- It emits very little smoke and leaves no ash
- It provides the most important lubricating agents and is used as a raw material for various petrochemical products
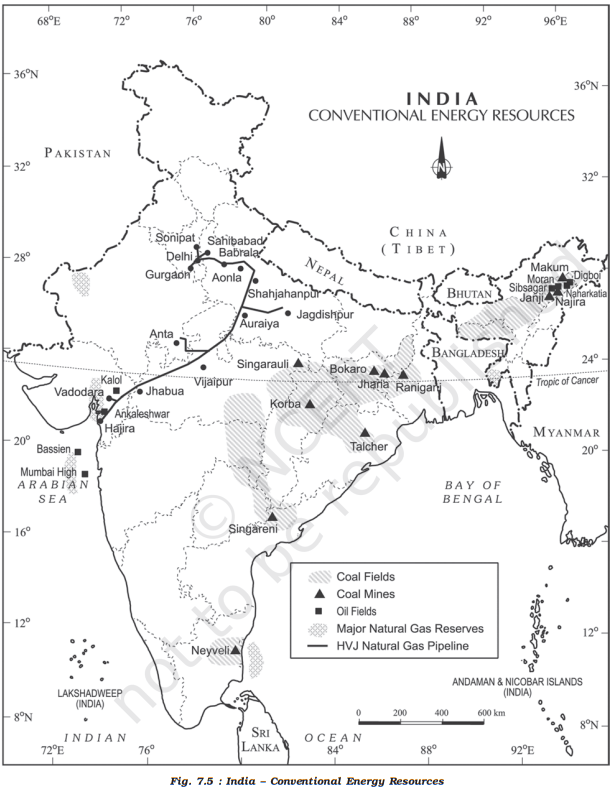
Oilfields in India | Oil Reserves in India
- North-eastern India:
- Major oilfields in Brahmaputra valley and neighboring areas including Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Tripura, Manipur, Mizoram, and Meghalaya
- Assam is the oldest oil-producing state in India
- Digboi is the oldest oil field in India; most oil is sent to the refinery at Digboi
- Naharkatiya field discovered in 1953; oil sent to oil refineries at Noonamati in Assam and Barauni in Bihar through pipeline
- Oil reserves found in Manabhaum, Kharsang, and Charai in Arunachal Pradesh
- Oil reserves found at Manmumbhanga, Manu, and Ampi Bazar in Tripura
- Western India Onshore field:
- Oil fields found around the Gulf of Khambat in Gujarat
- Main oil belt extends from Surat to Amreli; main producing districts include Kachchh, Vadodara, Bharuch, Surat, Ahmedabad, Kheda, and Mehsana
- Important oilfields include Ankleshwar, Lunej, Kalol, Nawgam, Kosamba, Kathana, Barkol, Mehsana, and Sanand
- Ankleshwar field is about 80 km south of Vadodara; capacity of 2.8 million tonnes per annum; oil sent to refineries at Trombay and Koyali
- Khambhat or Lunej field drilled in 1958; annual production of 15 lakh tonnes of oil and 8-10 lakh cubic metres of gas; total reserves estimated at 3 crore tonnes
- Ahmedabad and Kalol field contains ‘pools’ of heavy crude trapped in chunks of coal
- Rajasthan:
- One of the largest on-land oil discoveries made in the Banner district of Rajasthan in 2004
- Two important discoveries, Sarswati and Rajeshwari, with a total of 35 million tonnes of in-place oil reserves were made earlier in 2002
- Western Coast Off-Shore Oilfields:
- Mumbai High is located on the continental shelf off the coast of Maharashtra; estimated reserves of about 330 million tonnes of oil and 37,000 million cubic metres of natural gas
- Production on a commercial scale began in 1976; production declined between 1989-90 and 1993-94 due to overexploitation
- Bassein is located to the south of Mumbai High; reserves may be higher than those of Mumbai High
- Aliabet is located at Aliabet Island in the Gulf of Khambhat; huge reserves found in this field
- East Coast:
- The basin and delta regions of the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Cauvery rivers hold great potential for oil and gas production, both onshore and offshore
- Narimanam and Kovilappal oilfields in the Cauvery on-shore basin in Tamil Nadu expected to produce about 4 lakh tonnes of crude oil annually
- Oilfields recently discovered in the Krishna-Godavari basin in Andhra Pradesh, which produces less than one percent of the total crude oil of India
- Probable Areas:
- Vast possibilities of finding oil from about one lakh sq km area of sedimentary rocks in different parts of the country
- Outstanding areas which hold possibilities of oil include Jawalamukhi, Nurpur, Dharamsala, and Bilaspur in Himachal Pradesh; Ludhiana, Hoshiarpur, and Dasua in Punjab; the Gulf of Mannar off the Tirun
Petroleum Refining
- India’s first oil refinery started in 1901 at Digboi in Assam
- Another refinery was built in 1954 at Tarapur in Mumbai
- India has a refinery hub with excess refining capacity, leading to exports of refined oil and petroleum products
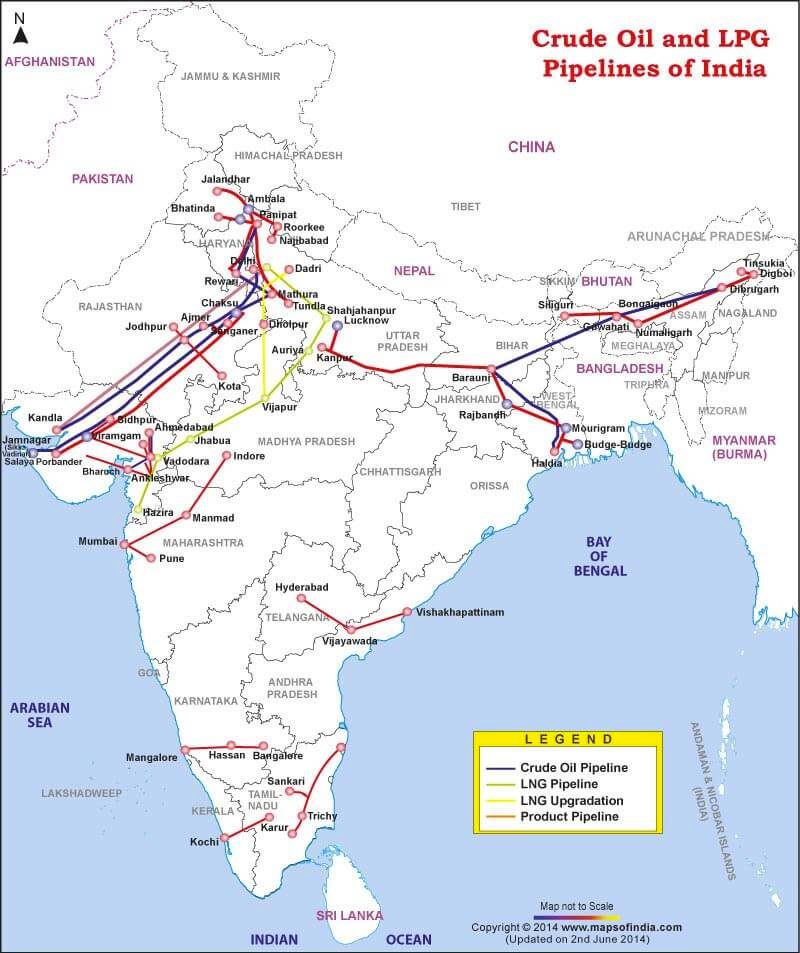
- Oil is transported to refineries through pipelines
- Advantages of pipelines:
- Ideal for transporting liquids and gases
- Can be laid through difficult terrains and underwater
- Requires little maintenance
- Safe, accident-free, and environmentally friendly
- Disadvantages of pipelines:
- Not flexible, can only be used for a few fixed points
- Capacity cannot be increased once laid
- Difficult to make security arrangements
- Detection of leaks and repairs are also difficult
- Crude Oil Pipelines
- Salaya-Mathura Pipeline (SMPL)
- Paradip-Haldia-Barauni Pipeline (PHBPL)
- Mundra-Panipat Pipeline (MPPL)
- Petroleum Product Pipelines
- Guwahati-Siliguri Pipeline (GSPL)
- Koyali-Ahmedabad Pipeline (KAPL)
- Barauni-Kanpur Pipeline (BKPL)
- Panipat-Delhi Pipeline (PDPL)
- Panipat-Rewari Pipeline (PRPL)
- Chennai – Trichy – Madurai Product Pipeline (CTMPL)
- Chennai-Bangalore Pipeline
- Naharkatia-Nunmati-Barauni Pipeline (first pipeline constructed in India)
- Mumbai High-Mumbai-Ankleshwar-Koyali Pipeline.
- Hajira-Bijapur-Jagdishpur (HBJ) Gas Pipeline
- Jamnagar-Loni LPG Pipeline
- Kochi-Mangalore-Bangalore pipeline
- Vishakhapatnam Secunderabad pipeline
- Mangalore-Chennai pipeline
- Vijayawada-Vishakhapatnam pipeline
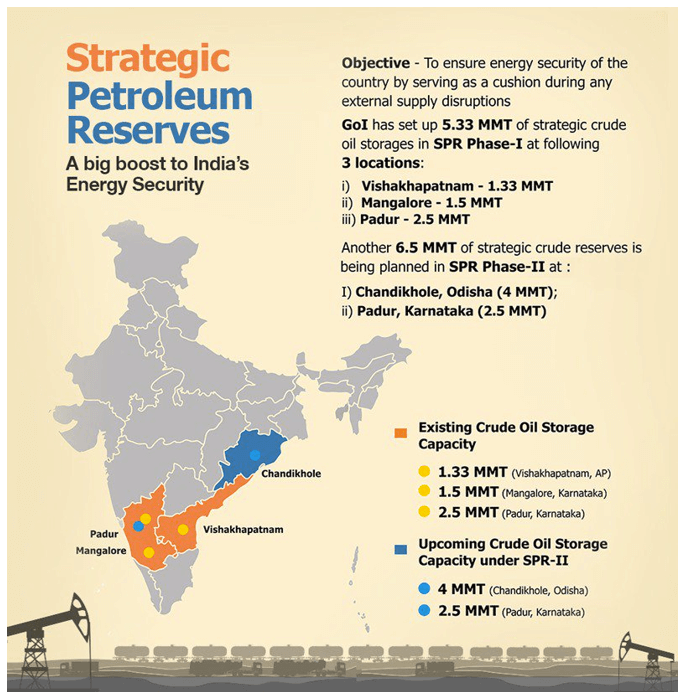
Strategic Petroleum Reserves
- Strategic petroleum reserves are stockpiles of crude oil to deal with oil-related crises.
- IEA countries must hold emergency oil stocks equivalent to at least 90 days of net oil imports.
- IEA members may decide to release these stocks to the market in case of severe oil supply disruption.
- India became an associate member of the IEA in 2017.
- India’s strategic crude oil storage facilities are located in Visakhapatnam, Mangaluru, and Padur.
- Two additional facilities have been approved for Chandikhol and Padur.
- The concept of dedicated strategic reserves was first mooted in the US after the OPEC oil crisis in 1973.
- Underground storage is the most economic method of storing petroleum products.
- The construction of the Strategic Crude Oil Storage facilities in India is being managed by ISPRL.
- ISPRL is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Oil Industry Development Board (OIDB) under the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas.
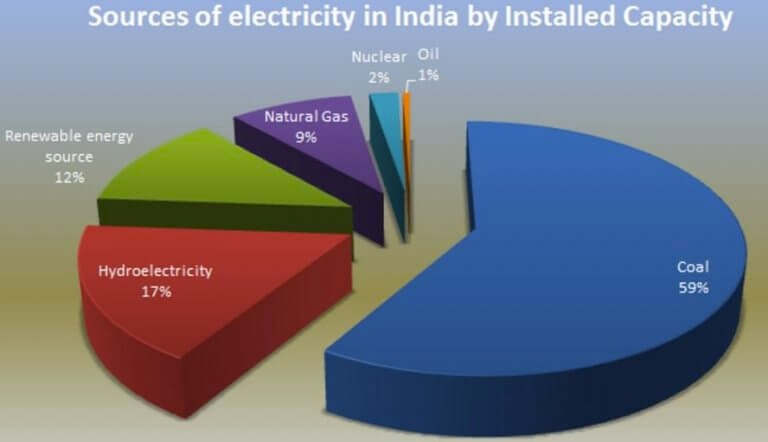
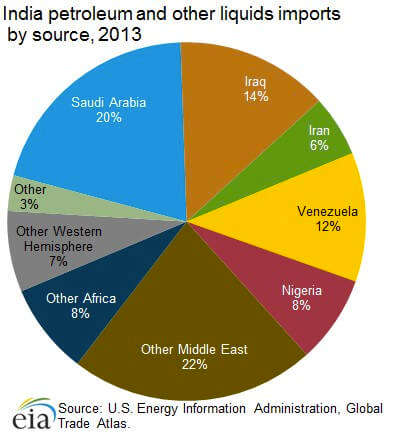
List of Major Oil Fields in India (with few details)
- DIGBOI:
- Located in the Dibrugarh district of Assam.
- Oldest oilfield in India with over 800 oil wells drilled.
- Most of the oil is sent to an oil refinery at Digboi.
- NAHARKATIA:
- Located 32 km southwest of Digboi at the left bank of Burhi Dihing river.
- 60 wells drilled, out of which 56 produce natural gas.
- Oil is sent to Noonmati (Assam) and Barauni (Bihar).
- MORAN-HUGRIJAN:
- Located about 40 km southwest of Naharkatiya.
- Discovered in 1953 and started production in 1956.
- 20 wells drilled, yielding both oil and gas.
- RUDRASAGAR:
- Located in the Upper Assam Valley.
- Discovered by ONGC and OIL in 1961.
- Oil deposits found in the Barail rocks.
- SIVSAGAR:
- Located in the Upper Assam Valley on the bank of the Brahmaputra.
- Once the capital of the Ahom rulers.
- Oilfields located at Lakwa, Lakhmani, Rudrasagar, Geleki, and Moran.
- ANKALESHWAR:
- Located 80 km south of Vadodara in Gujarat, discovered in 1958.
- Ankleshwar anticline is about 20km long and 4 km wide.
- Pandit Nehru called it “the Fountain of Prosperity.”
- Oil is sent to Trombay and Kalol refineries.
- KALOL:
- 25 km north of Ahmedabad
- ‘pools’ of heavy crude trapped in coal at 1400 m depth
- Oil production started in 1961
- NAWGAM:
- 24 km south of Ahmedabad
- Yields both oil and gas
- MEHSANA:
- North of Ahmedabad
- Famous for milk production and petroleum
- Established in 1967
- Highest onshore-producing asset of ONGC
- SANAND:
- 16 km west of Ahmedabad
- Produces both oil and gas
- Tata Nano and Ford car plants located here
- LUNEZ:
- Located 60 km west of Vadodara
- First drilled in 1958 by ONGC
- Produces both oil and gas
- Estimated reserves – 30 million tonnes of oil
- Oil – 15 lakh tonnes / year
- Gas- 8-10 lakh cubic m/year
- KOSAMBA:
- Located between Narmada and Tapi rivers in the Surat district of Gujarat
- ONGC produces oil here
- KATHANA:
- North Kathana is a 7 sq. km oil field located near Khambhat town in Gujarat
- Oilfields are managed by the GSPC
- ALIABET:
- Located in the Gulf of Khambhat on the Aliabet Island about 45 km off Bhavnagar
- Huge reserves have been found
- BASSEIN:
- Located to the south of the Mumbai High
- Recently discovered which may prove to be higher than those of the Mumbai High
- Production has already been started
- MUMBAI HIGH:
- Located 176 km north-west of Mumbai on the continental shelf
- Reserves – 330 million tonnes of oil and 37,000 million cubic meters of natural gas
- Sagar Samrat- specially designed platform for oil extraction
- Produces about two-third crude oil of India
- RAWA:
- Located in Krishna – Godawari off–shore basin
- Expected to produce 1 to 3 million tonnes of crude oil annually
- Developed by Cairn India in partnership with ONGC, Videocon and Rawa Oil
- Produces both oil and gas
- K-G BASIN:
- The basin and delta of Krishna and Godavari hold great potential of oil and gas
- Rawa field, Reliance’s gas field
- Extensive exploration work is going on in the region
- NARIMANAM AND KOVILAPPAL:
- Located in the Cauvery on–shore basin
- Expected to produce about 4 lakh tonnes of crude oil annually
- Oil will be refined at the Panaigudi refinery near Chennai
- MANGLA:
- Major oilfields located in Rajasthan in the Barmer district
- Consists of over 16 separate oil and gas fields of which the major three are Mangla, Bhagyam and Aishwarya
- The current operator of the fields is Cairn India.

0 Comments