- Plateau in the world- The Plateaus are built over millions of years as pieces of Earth’s crust smash into each other, melt, and gurgle back toward the surface.
- The term Plateau can be defined as the upland which has at least one side of a very steep slope standing well above the neighboring surface and whose upper part is extensively flat.
- The most significant deciding factor of the Plateau is the flatness of its top rather than the height.
List of Major Plateaus of the World
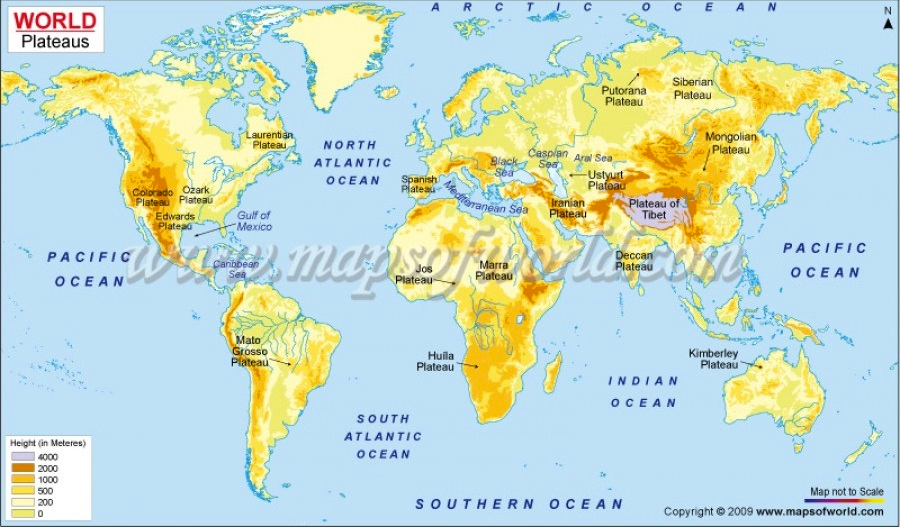
Colorado Plateau:
- Includes Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico.
- Divided by the Colorado River and the Grand Canyon.
- Largest plateau in America, covering an area of 337,000km2.
- Highest elevation is about 2,450m above sea level.
- Intermontane plateau with mesas and buttes found at many places.
- Known for the emergence of Artesian wells.
Columbia Plateau:
- Located in parts of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho.
- Surrounded by the Cascade Range and Rocky Mountains.
- Coated in basalt lava from volcanic eruptions (Flood Basalt Plateau).
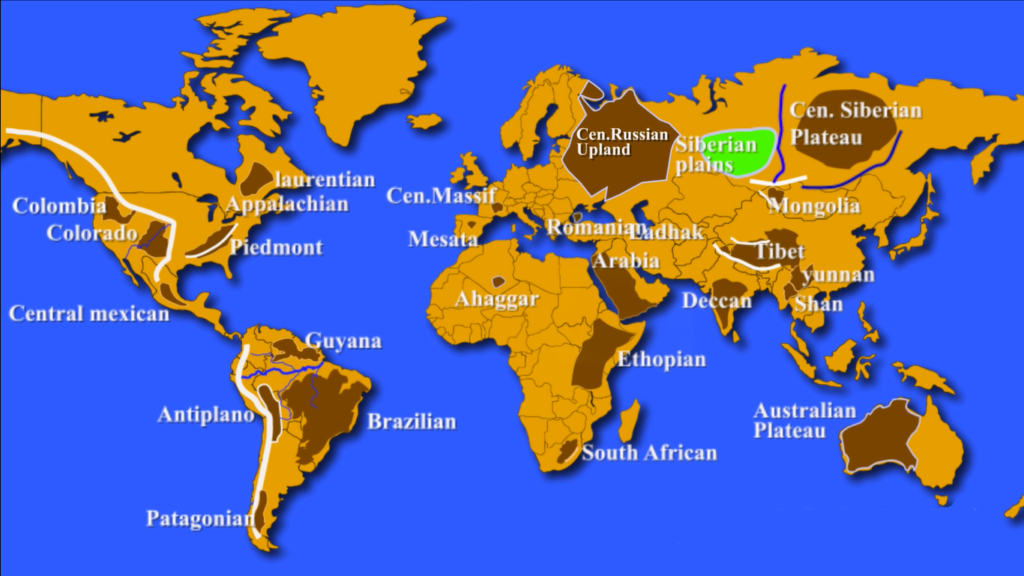
Appalachian Plateau:
- Series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains.
- Northwestern part of the Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York to Alabama.
Piedmont Plateau:
- Plateau region located in the Eastern United States.
- Situated between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York to central Alabama.
- Consists of the Gettysburg-Newark Lowlands, the Piedmont Upland, and the Piedmont Lowlands sections.
Laurentian Plateau:
- Canadian Shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that forms the ancient geologic core of the North American continent.
- Fine quality of iron-ore is found here.
Central Mexican Plateau:
- Also known as the Mexican Altiplano.
- Large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico.
- Extends from the United States border in the north to the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt in the south.
- Bounded by the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental to the west and east, respectively.
Altiplano Plateau:
- Located in west-central South America between two ranges of the Andes Mountain
- Major area for tin reserves
- Capital of Bolivia, La Paz and Sucre, are situated on this plateau
Guyana Highland:
- Part of the Guyana Shield in northeast South America
- One of the oldest land surfaces in the world
- A 1.7 billion-year-old Precambrian geological formation
Brazilian Highland:
- Covers most of the eastern, southern, and central portions of Brazil
- Divided into three plateaus: Atlantic, Southern, and Central
- Once almost completely covered by the Atlantic Rainforest
Patagonian Highland:
- Located in the southern part of Argentina
- A rain shadow desert plateau
- Important region for sheep rearing
Central Massif:
- Located in the middle of southern France
- Consists of mountains and plateaus
- Famous for grapes cultivation
Mesata:
- One of the basic geographical units of the Iberian Peninsula
- Consists of a plateau covering a large part of the latter’s interior
Transylvanian Plateau:
- Plateau in central Romania
- Almost entirely surrounded by the Carpathian Mountains
- Includes the Transylvanian Plain
Hardangervidda Plateau:
- One of the largest plateaus in Europe
- Located in western Norway, about 200 km west of Oslo
- Northwest of the plateau is bordered by one of the largest glaciers of Norway
Central Russian Upland:
- Upland area of the East European Plain
- Undulating plateau with an average elevation of 230–250 m
- Highest peak is measured at 293 m
- Southeastern portion is known as the Kalach Upland
Tibetan Plateau:
- Highest, largest, and most famous plateau in the world
- Located in South-Central Asia, stretches through Tibet, China, and India
- Covers an area of 2,500,000 km2 with a flat valley floor at about 16,000 feet above sea level
- Formed due to collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian tectonic plates
- Surrounded by mountains to the south (Himalayan Range), northeast (Kunlun Range), and west (Karakoram Range)
Mongolian Plateau:
- Part of the Central Asian Plateau
- Approximately 3,200,000 square kilometers in area
- Bounded by the Greater Hinggan Mountains in the east, Yin Mountains to the south, Altai Mountains to the west, and Sayan and Khentii mountains to the north
- Includes the Gobi Desert and dry steppe regions
- Elevation of roughly 1,000 to 1,500 meters, with lowest point in Hulunbuir and highest point in Altai
Central Siberian Plateau:
- Occupies great part of central Siberia between Yenisei and Lena rivers
- Located in the Siberian Platform and extends over an area of 3,500,000 km2
- Bounded to the south by Altai Mountains, Salair Ridge, Kuznetsk Alatau, Eastern and Western Sayan Mountains, and other mountains of Tuva
- Bounded to the north by North Siberian Lowland and to the east by Central Yakutian Lowland and Lena Plateau
- Surface characterized by alternation of wide plateaus and ridges, covering one-third of Siberia
Deccan Plateau:
- Large plateau in southern India
- Bordered by Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats mountain ranges
- Includes Deccan Traps, the largest volcanic feature on Earth
- Deccan Traps cover an area of 500,000 square kilometers and contain unique fossils
- Rich in minerals including mica, iron ore, diamonds, gold, and other metals
Yunnan Plateau:
- Highland region in southwest China
- Primarily located in the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou
Shan Plateau:
- Crystalline massif in eastern Myanmar (Burma)
- Part of the Indo-Malayan mountain system
- Crossed by the Salween River in the east and bordered by the Irrawaddy River in the west
- Average elevation between 2,500 and 4,000 feet (750 and 1,200 m)
- Seamed and ribbed by mountain ranges
Arabian Plateau:
- Oligocene sub-horizontal regional planation surface in the western half of the Arabian Peninsula
- Required a prominent uplift since the Late Eocene to reach its present elevation of about 1 km
Anatolian Plateau:
- Intermontane plateau in Turkey
- Lies between Pontiac and Taurus Mountain ranges
- Tigris-Euphrates Rivers flow through the plateau
- Precious wool producing Angora goats found here
Ethiopian Plateau:
- Rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in northeast Africa
- Largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent
- Little of its surface falls below 1,500 m, while the summits reach heights of up to 4,550 m
East African Plateau:
- Large plateau in eastern part of central Africa in Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania
- Elevation mostly between 1000 and 1500 meters
- Subdivided into zones consisting of mountain ranges, tablelands, and rift valleys
Table Mountain:
- Prominent landform in Cape Town, South Africa
- Located at the northern end of the Sandstone Mountain Range
- Level plateau measuring 3 km from side to side
Ahaggar Plateau:
- Large plateau in the north center of the Sahara, North Africa
- Height above 3,000 feet (900 m), culminating in Mount Tahat (9,573 feet [2,918 m]) in southeastern Algeria
Katanga Plateau:
- Farming and ranching region in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Famous for copper production
- Other minerals mined here include cobalt, uranium, zinc, silver, gold, and tin.
Western Plateau:
- Australia’s largest drainage division.
- Covers two thirds of the continent.
- Composed of remains of the ancient rock shield of Gondwana.
- Mostly flat sandy or stony desert with sparse shrub or grass cover.
Kimberley Plateau:
- Located in northern Western Australia.
- Extends from northwest Indian Ocean coast to the Fitzroy River and east to the Ord River.
- Made of volcanic eruption.
- Rich in minerals like iron, gold, lead, zinc, silver, and diamonds.
- Used for mining and cattle rearing.
Atherton Tableland:
- Located in Queensland, Australia.
- Covers an area of 32,000km2 with elevation of 500 to 1,280m above sea level.
Antarctic Plateau:
- Located in Central Antarctica, crossing parts of the South Pole and Amundsen Scott Station.
- Covers an area of 1,000km2 and has its highest elevation of about 3,000m above sea level.
Potohar Plateau:
- Located in northeastern Pakistan.
- Bordered by Jehlum River to the east, Indus River to the west, Margalla Hills and Kala Chitta Range to the north, and Salt Range to the south.
- Encompasses four districts: Jehlum, Chakwal, Rawalpindi, and Attock.
Mascarene Plateau:
- An oceanic plateau in the Indian Ocean between Seychelles and Mauritius Islands.
Loess Plateau:
- Located in China.
- Soil composed of fine particles brought by wind.
- Highly productive for crop growth along the Yellow River.

0 Comments