Atomic Minerals
- India has significant reserves of atomic minerals, including uranium and thorium, as well as beryllium, lithium, and zirconium.
- Thorium is mainly derived from monazite, which contains 10% thoria and 0.3% urania. Another mineral carrying thorium is thorianite.
- India’s nuclear power plants use nuclear fuel processed in three stages: uranium, products obtained from processed nuclear fuel, and thorium.
- India has the largest deposits of thorium in the world and aims to become self-reliant in nuclear fuel supply by transitioning to the third stage of nuclear fuel consumption.
- India produces about 2% of the world’s uranium, with total reserves estimated at 30,480 tonnes.
- Uranium deposits in India are found in crystalline rocks, with 70% located in Jharkhand. Uranium deposits also occur in the Singhbhum and Hazaribagh districts of Jharkhand, Gaya district of Bihar, and in sedimentary rocks in the Saharanpur district of Uttar Pradesh.
- Mines of Atomic minerals are given below:
Other minerals having atomic content with economic viability:
- Monazite sands, which contain over 15,200 tonnes of uranium, are found on both the east and west coasts of India and in some places in Bihar. The largest concentration of monazite sand is on the Kerala coast.
- Ilmenite deposits are found in the state of Jharkhand.
- Beryllium oxide, used as a moderator in nuclear reactors, is found in Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Zirconium is found along the Kerala coast and in alluvial rocks of Ranchi and Hazaribagh districts of Jharkhand.
- Lithium, a light metal, is found in lepidolite and spodumene. Lepidolite is widely distributed in the mica belts of Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan, as well as in the Bastar region of Chhattisgarh.
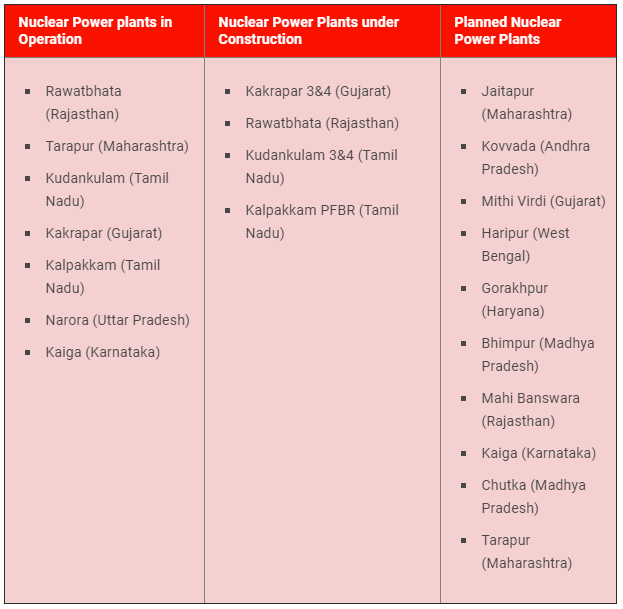
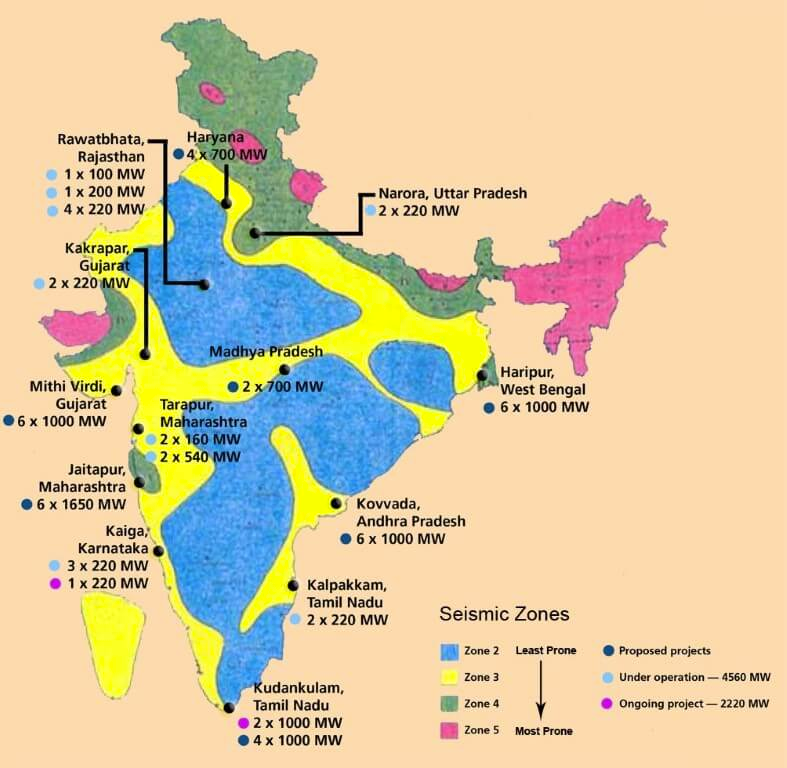
Five centers of Atomic energy in India are:
- The Tarapur Nuclear Reactor in Maharashtra, Western India, is the oldest nuclear facility in India, having commenced commercial operations in 1969.
- The Rana Pratap Sagar Plant is located in Kota Industrial Complex and eastern Rajasthan.
- The Narora Nuclear Reactor in Uttar Pradesh, Northern India has two PHWR, with a total capacity of 440MW. Unit 1 was installed in January 1991, and unit 2 following in July 1992.
- The Kalapakkam Nuclear Power Plant in Tamil Nadu first began operating in 1984 and currently has two 235MW reactors, with two more reactors of 500MW and 600MW to be added at a later date.
- The Kakarapar Atomic Power Plant in Gujarat, Western India has two PHWR reactors with a total installed capacity of 440MW. The two reactors were completed in May 1993 and September 1995, respectively.
Uranium
- Uranium is a silvery-gray metallic radioactive chemical element.
- Uranium, thorium, and potassium are the main elements contributing to natural terrestrial radioactivity.
- Uranium has the chemical symbol U and atomic number 92.
- Uranium isotopes in natural uranium are 238U (99.27%) and 235U (0.72%).
- All uranium isotopes are radioactive and fissionable. Only 235U is fissile (will support a neutron-mediated chain reaction).
- Traces of Uranium are found everywhere, but commercial extraction is possible only in locations where the proportion of Uranium is adequate. There are very few such locations.
Distribution of Uranium Across the World
- Largest viable deposits of uranium are found in Australia, Kazakhstan, and Canada.
- Important mines in Australia include Olympic Dam and the Ranger mine.
- High-grade deposits are only found in the Athabasca Basin region of Canada.
- Other important uranium mining sites in Canada include Cigar Lake and McArthur River basin.
- The Chu-Sarysu basin in central Kazakhstan accounts for over half of the country’s known uranium resources.
- Kazakhstan produces the largest share of uranium from mines (42% of world supply from mines in 2019), followed by Canada (13%) and Australia (12%).
Uranium in India
- India has limited reserves of uranium and imports most of its needs from Russia, Kazakhstan, France, and others.
- India is trying to import uranium from Australia and Canada, but there are concerns regarding nuclear proliferation and related issues that need to be addressed.
- Some quality reserves of uranium were recently discovered in parts of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana between Seshachalam forest and Sresailam.
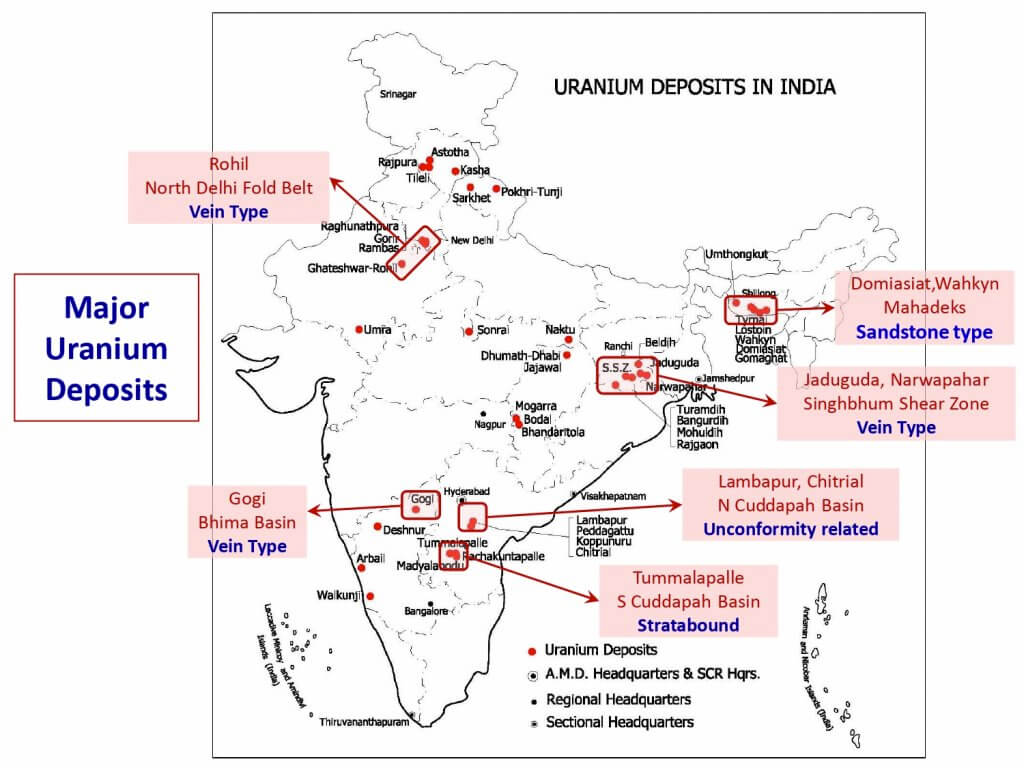
Uranium Mines
- Jharkhand
- Jaduguda, Bhatin, Narwapahar, Bagjata, Turamdih, Banduhurang, Mohuldih
- Meghalaya
- Kylleng, Pyndeng-Shahiong (Domiasiat), Mawthabah, Wakhym
- Andhra Pradesh
- Lambapur-Peddagattu, Tummalapalle
- Jadugora
- Located in the Singhbhum district of Jharkhand
- The first uranium mine opened by UCIL in 1968
- Ores are treated in a mill located a Jaduguda itself
- UCIL is located here itself
- Tummalapalle
- It is located in the YSR district of Andhra Pradesh.
- The combined reserve in 49000 tonnes of uranium. It can be increased three times, which will make it the mine with the largest uranium deposits in the world.
- Mohuldih
- It is located in the Seraikella – Kharsawan district of Jharkhand.
- It was commissioned by UCIL on 17 April 2012.
- The ore produced here were be sent to Turamdih Processing Plant.
- Turamdih
- It is located in the East Singhbhun district of Jharkhand.
- It has 7.6 million tonnes of uranium are reserves.
- A new uranium procession plant has been constructed here.
Thorium
- Thorium is a chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90.
- It occurs naturally in large quantities, like uranium.
- Thorium metal is silvery and tarnishes black in air.
- Thorium is weakly radioactive, and all of its isotopes are unstable.
- Thorium-232 is the most stable isotope of thorium and makes up nearly all natural thorium.
- Thorium is about three to four times more abundant than uranium in the Earth’s crust.
- Thorium is mainly refined from monazite sands, which contain 2.5% thorium.
- Thorium is predicted to replace uranium as nuclear fuel in nuclear reactors.
- However, only a few thorium reactors have been completed so far.
Monazite – Rare Earth Metals
- Monazite is a phosphate mineral that contains rare earth metals.
- Rare earth elements are important for many modern technologies, such as consumer electronics, clean energy, and national defense.
- Rare earth elements have unique properties that help reduce weight, emissions, and energy consumption, or enhance efficiency, performance, and durability.
- There are 17 rare earth elements, including the 15 lanthanides, scandium, and yttrium.
Advantages of Thorium
- Weapons-grade fissionable material (U-233) is harder to retrieve safely from a thorium reactor, as it contains U-232, a strong source of gamma radiation that makes it difficult to work with.
- Thorium reactors produce far less waste than present-day reactors, with 10 to 10,000 times less long-lived radioactive waste.
- Thorium reactors can burn up most of the highly radioactive and long-lasting minor actinides that make nuclear waste from Light Water Reactors a nuisance to deal with.
- Thorium reactors are cheaper because they have higher burn-up.
- Thorium mining produces a single pure isotope, whereas the mixture of natural uranium isotopes must be enriched to function in most common reactor designs.
- Thorium cannot sustain a nuclear chain reaction without priming, so fission stops by default in an accelerator-driven reactor.

0 Comments