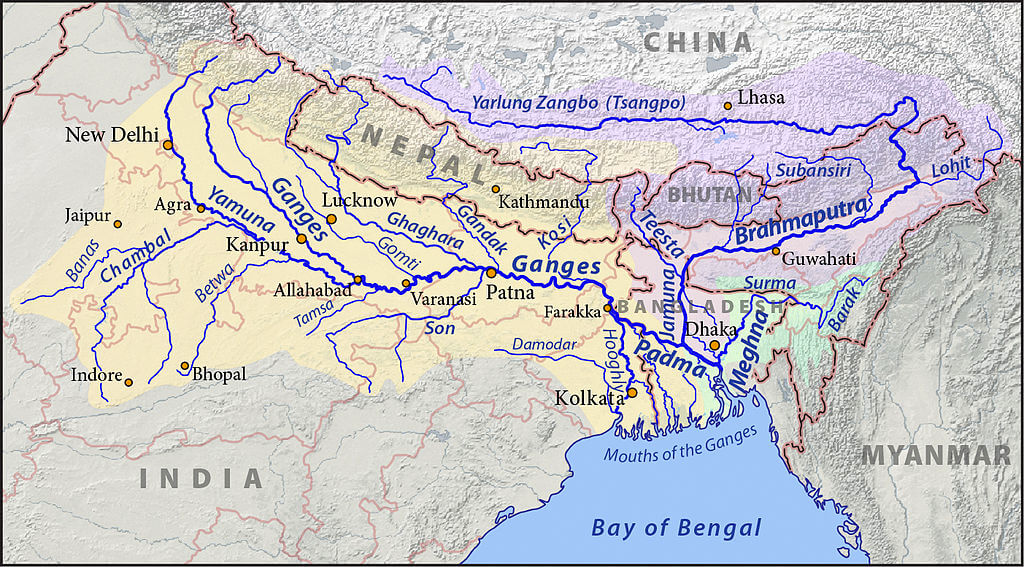
- Where is Yamuna River located? The Yamuna River starts at the Yamunotri Glacier, located on the southwestern slopes of Banderpoonch peak in the Mussoorie range of the lower Himalayas.
- Yamuna River Route – It flows through several states, including Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, and Delhi, before merging with the Ganga River at Triveni Sangam in Allahabad.
- Yamuna is the Largest Tributary of -The Yamuna is the largest tributary of the Ganga River in the northern plains.
- Tons is a tributary of which river? Its main affluent in the upper reaches is the Tons River, which also originates from the Bandarpunch glacier.
- Tons River Water Volume – The Tons River joins the Yamuna River below Kalsi, where the water carried by the Tons River is twice that of the Yamuna River.
- Length of Yamuna River – The Yamuna River is 1,376 km long from its origin to its confluence with the Ganga River in Allahabad.
- The Yamuna River creates the highly fertile alluvial. Yamuna-Ganges Doab region between itself and the Ganga River in the Indo-Gangetic plain.
- Route of Yamuna River – Many cities, including Bhagpat, Delhi, Noida, Mathura, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Hamirpur, and Allahabad, are located on the banks of the Yamuna River.
Major Tributaries of Yamuna River
Tons
- The Tons River is the longest tributary of the Yamuna River.
- It flows through Garhwal, the western part of the Himalayan state of Uttarakhand.
- The river originates at an elevation of 3900 m and joins the Yamuna below Kalsi near Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
- It is one of the major perennial rivers in the Indian Himalayas.
Giri
- The Giri River is a significant tributary of the Yamuna River.
- It provides the main water source for the South-Eastern region of Himachal Pradesh.
- The river is well-known in the Jubbal and Rohru hills, which rise from Kupar peak just above Jubbal town.
- After flowing across the heart of the Shimla hills, the river runs in a southeastern direction and divides the Sirmaur district into two equal parts known as Cis-Giri and Trans-Giri regions before joining the Yamuna upstream of Paonta below Mokkampur.
Hindon
- The Hindon River is a significant tributary of the Yamuna River and is situated between the Ganga River on the left and Yamuna River on the right.
- It originates from the upper Shiwalik region of the Lower Himalayas and is solely dependent on rainfall, with a catchment area of around 7,083 sq. km.
- The river spans a length of approximately 400 km and its width varies from 20 m to 160 m.
Chambal
- Chambal River is also called Charmanwati or Charmawati.
- It originates from Janapao Hills of the Vindhya range, located 15 km West-South-West of Mhow in Indore district in Madhya Pradesh.
- The river is 960 km long.
- It is used for hydropower generation at several dams, including Gandhi Sagar dam, Rana Pratap Sagar dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam, and the Kota Barrage.
- Due to poor rainfall and severe erosion, the river flows much below its banks, and the Chambal Valley has many deep ravines, leading to the formation of badland topography.
- Dams on the Chambal:
- Gandhi Sagar dam: first of four dams on the Chambal River, on the Rajasthan-Madhya Pradesh border
- Rana Pratap Sagar dam: located 52 km downstream of Gandhi Sagar dam, across the Chambal River in Chittorgarh district in Rajasthan
- Jawahar Sagar Dam: third dam in the Chambal Valley Projects, located 29 km upstream of Kota city and 26 km downstream of Rana Pratap Sagar dam
- Kota Barrage: fourth in the Chambal Valley Projects, located about 0.8 km upstream of Kota City in Rajasthan; diverts water released after power generation at Gandhi Sagar dam, Rana Pratap Sagar dam, and Jawahar Sagar Dams for irrigation in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh through canals.
- Keoladeo National Park is supplied with water from the Chambal River irrigation project.
Banas
- Also known as ‘Van Ki Asha’ (Hope of forest),
- Originates in the Aravalli Range in Rajsamand District of Rajasthan.
- The cities of Nathdwara, Jawanpur, and Tonk lie on the river.
- Its entire, course is in Rajasthan only.
Kali Sindh
- Flows in the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh, that joins the Chambal River near Sawai Madhopur In Rajasthan
- Kali Sindh originates in Madhya Pradesh.
Parbati
- Originates in the northern slopes of the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh, flows through Kota District and Jhalawar District of Rajasthan.
- Runs for about 436km and has a catchment area of nearly 3,070 sq miles.
- Joins the right bank of the Chambal
- The city of Guna (MP) lies on it.
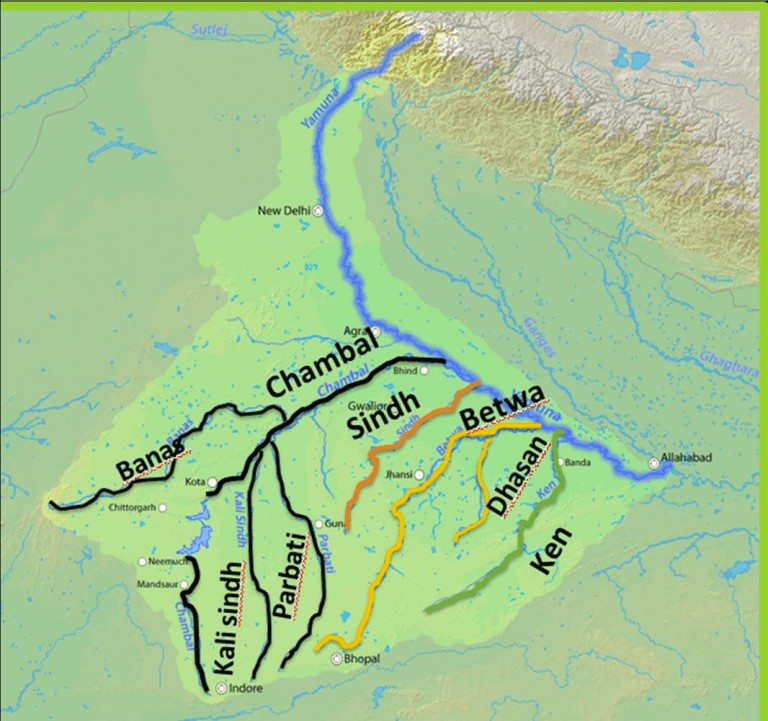
Sindh
- The Sindh originates on the Malwa Plateau in Vidisha district.
- Flows north-northeast through the districts of Guna, Ashoknagar, Shivpuri, Datia, Gwalior, and Bhind in Pradesh
- Join the Yamuna River in Etawah District, Uttar Pradesh
- Flows through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
Betwa
- Also called as Vetravati
- Rises in the Vindhya Range north of Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh.
- The confluence of the Betwa and the Yamuna Rivers takes place in the Hamirpur town in Uttar Pradesh.
- Dhasan is the main tributary.
- Rajghat Dam located on the river.
Dhasan River
- It is a right-bank tributary of the Betwa River.
- It originated in Raisen District in Madhya Pradesh.
- Flows through Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
Ken
- The Ken River originates from the slopes of Kaimur Range in Jabalpur district in Madhya Pradesh
- Merge with the Yamuna near Fatehpur in UP.
- The Ken Valley separates the Rewa Plateau from the Satna Plateau.
- The Ken River passes through Penna National Park.
Important places through which Yamuna passes
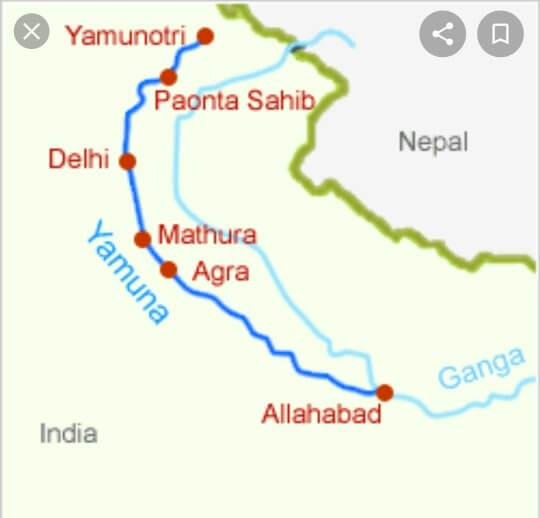
- State: Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi
- Cities: Delhi, Noida, Mathura, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Kalpi, Hamirpur, and Prayagraj lie on its banks.
Learn about the Indus, Godavari, and Brahmaputra rivers—key for UPSC geography prep.

0 Comments